Marketing 5.0 Perspective – 2: How can companies practically apply Marketing 5.0 to enhance their marketing capabilities?
Previously, in “Marketing 5.0 – Part 1: Ahead of the Market, This is How Entrepreneurs and Marketers Do It ,” we discussed the concepts of “Data Marketing” and “Predictive Marketing” proposed in the book. In this article, we will continue to discuss the internal business skills of “Agile Marketing” and the application skills of “Scenario Marketing” and “Enhanced Marketing,” and how they can help companies grow in internal operations, marketing, and customer maintenance.
Agile Marketing : Stimulating Internal Team Upgrades
Companies that commonly implement agile marketing include those in industries with short product lifecycles, such as fast fashion apparel and 3C technology. However, nowadays, other companies also face the reality of customers and competitors actively seeking innovation and change; a company’s brand/products are constantly challenged in the market. Adopting agile marketing as a business strategy is crucial to cultivating the team’s ability to adapt to rapidly changing strategies and navigate the fast-paced market. (Further reading: McKinsey & Company – Agile Marketing Strategy )
1. Facilities and knowledge tailored to the needs of the marketing team:
Enterprises must have a foundation of hardware and software, storage space, IT technology, digital knowledge, and data analysis technology that are geared towards the needs of marketing personnel in order to develop capabilities such as robot collaboration, algorithm analysis, and virtual-physical integration.
2. Remote collaboration capability:
Enterprises must be able to:
(1) Enable employees to work, collaborate, and communicate with customers remotely with zero resistance.
(2) To ensure customers receive immediate responses and seamless switching between media while browsing, shopping online and offline, experiencing products, and obtaining information/answers. (This includes physical spaces, computers, mobile devices, online meeting rooms, online exhibition spaces, etc.)
3. Robots & Soft Robots:
Robots don’t necessarily mean “a humanoid machine serving customers.” Businesses should also have software robots on hand to automate repetitive processes . In operational administration, tasks like invoicing, payments, and human resource management can be handled by software robots on a scheduled basis.
For example, using robots to assist in Customer Relationship Management (CRM), as we previously discussed using data marketing and predictive marketing to establish customer segmentation, we can then set the time and action for the software robot to trigger customer interactions, automatically sending different pre-made marketing ads to targeted members and potential customers. This type of manpower-saving approach is becoming increasingly popular in enterprises. What we can do is continuously refine the robot’s tasks. For example, we can analyze the effectiveness of each advertising channel (EDM and different social media platforms) for each CRM target group, and further set different actions for each customer. The robot can then automatically determine whether to advertise this time and whether it is cost-effective.
Context Marketing : Personalized experiences that showcase brands and products through interactive displays.
The market competitiveness of “how to interact with the brand” has gradually surpassed that of the product itself . Therefore, companies should create perfect scenario marketing tools for their brands and products to interact with consumers through information and immersive experiences. When customers want to find answers, have conversations, or enjoy sensory experiences, companies should be ready.
Martech: Practical Scenario-Based Marketing for Businesses
1. Chatbot “Natural Language Processing”:
What is Natural Language Processing?
In the human subconscious, multiple thoughts are brewing and occurring in the mind at the same time, and language is also prone to presenting a variety of different fragments of information jumping back and forth; however, chatbots with natural language processing capabilities optimize themselves through data collection, advancing from simply answering mechanical questions to being able to chat with people; even if customers make typos, ask incoherent questions, or misplace information in their inquiries, the robot can still understand the customer’s questions from the fragmented information and provide responses that meet the customer’s needs .
2. Interactive Games:
Businesses design mini-game apps for their brands, incorporating tasks, character development, and other simple and easy-to-learn gameplay elements. These games offer tangible benefits to players, aiming to encourage users to “spend just a little time each day” to maintain a continuous connection with the brand . They effectively generate buzz, attract new customers, and solidify the brand’s position in the minds of customers. They also encourage customers to proactively follow up on new product launches and take advantage of promotional activities.
In 2018, Pinduoduo’s “Duoduo Orchard” was a very successful example of game marketing. Duoduo Orchard targeted consumers who bought “food ingredients and daily necessities” on the Pinduoduo platform (such as housewives and young professionals sharing a room). The simple “watering” action took less than a minute each day, but in the end, a box of real fruit was delivered to their door! As of 2021, statistics showed that there were 60 million players who regularly entered the game every day.
3. Smart sensing facilities:
For example, when beacons are placed in large shopping malls and amusement parks, the first impression for consumers is that beacons are a thoughtful service that guides people to avoid getting lost while shopping. However, if functions such as “add to shopping list” and “make an appointment” are added to the navigation, the service can be used to capture the subconscious mind of users. In physical sales venues, beacons can quickly guide customers to the store to select products, shortening the customer journey map to the shortest possible length.
(Further reading: E-Da World deploys Beacon technology to help shoppers navigate without getting lost, boosting both customer satisfaction and sales )
4. Products used in virtual reality teaching:
While AR and VR were primarily used for entertainment in the past, VR is now increasingly being used for advertising, sales demonstrations, and CRM strategies. For example, the startup iStaging ‘s online home and car viewing service blends virtual reality with live customer service . This allows them to provide consumers with a strong impression of the physical product through 360° panoramic visual displays and tactile simulations while they are still considering a purchase. This strengthens consumers’ trust in the product as they compare different options, and combined with live customer service explanations, it successfully sells products remotely.
5. Artificial intelligence computation:
As we discussed before, using data marketing and predictive marketing algorithms for targeted advertising and personalized recommendations falls into this category. Common examples include Amazon’s AI-powered book recommendations and YouTube’s ad push notifications. Besides tracking human online activity, algorithms can also use location services to track real-world behavior, providing frequently used information and product updates . For instance, Uber and Lyft ride-hailing services update their fares based on peak hours and population density, or food delivery platforms provide real-time updates to customers waiting at home about how long their meals will take.
Agmented Marketing :
Can be seen as an accelerator for integrating data marketing, predictive marketing, and contextual marketing.
As artificial intelligence continues to advance, computers can quickly take over “single tasks” from humans, such as detecting trigger points and analyzing data, often performing even better than humans. However, relying 100% on machines lacks the warmth of human interaction and the ability to flexibly adapt decisions based on individual events, potentially leading to disasters (such as the 2020 Amazon HR system incident where the algorithm automatically fired a large number of employees). Therefore, the most suitable approach for businesses today remains for humans to lead the initiation of actions and make final decisions, while computers provide assistance in various ways to accelerate the implementation of those decisions.
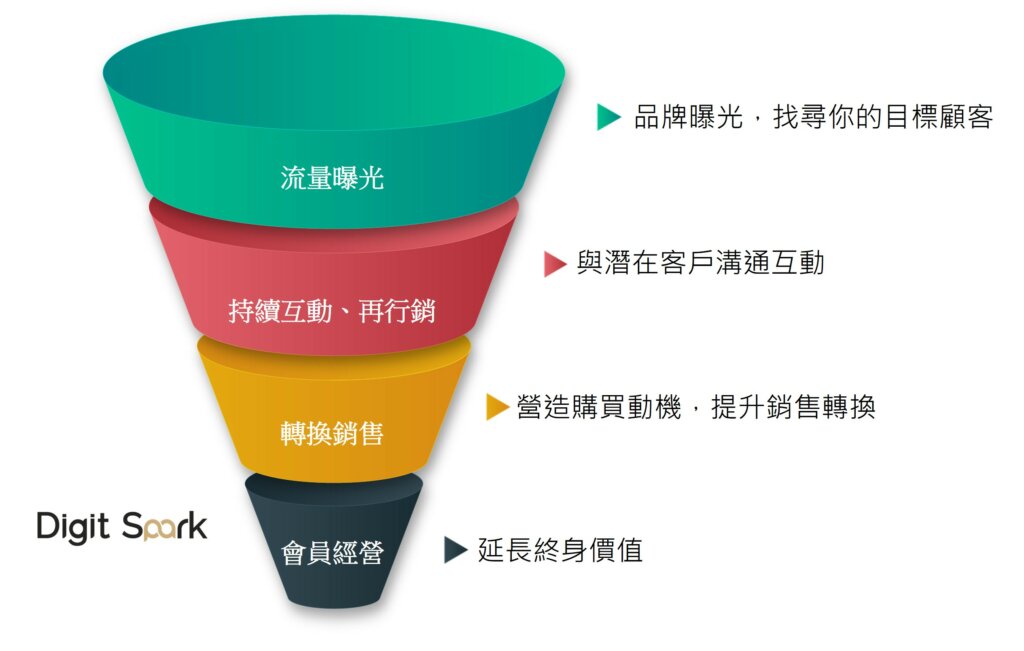
Using the marketing funnel as an example, how can we effectively enhance marketing?
Throughout the sales process, we use a funnel to implement ” identifying the customer lifecycle ” and “maintaining customer loyalty” in stages. The purpose of using enhanced marketing at different stages of the process is to leverage technological tools to help people (brands) and people (consumers) interact more effectively.
1. Traffic exposure stage:
(1) Through extensive algorithm data analysis, we can segment the markets we intend to enter and attract a wide range of potential customers.
(2) Build and optimize the SEM and SEO search volume of the enterprise brand and expand the reach of the brand/product.
2. Interactive remarketing stage:
(1) For each brand message sent to the target customer group, continuously use data analysis to optimize “what information should be given to this customer in the most useful way”, and move towards personalized marketing.
(2) Providing personalized scenario marketing for customers, the first step is to have AI customer service that can respond to consumers in the most intuitive and humane way.
3. Transitioning to the sales stage:
In the first two stages, data can also help us estimate customer lifetime value (when they will no longer consume our products); at the same time, frontline sales staff will work with the digital tools designed by the company (such as apps, online course resources, FAQ helpers, and member profile databases) to provide convenient services to customers, but to build an emotional connection with customers, human intervention is still indispensable.
4. Membership Management Stage:
Understanding human nature is crucial for building customer loyalty and extending customer lifetime value. For example, computers can help us conduct extensive surveys on customer satisfaction, but how should brands adjust their strategies after compiling this information? Furthermore, how to cultivate VIP relationships using reward mechanisms and tiered gold/platinum memberships relies on human emotional empathy and experience for judgment , with technological tools as supplementary tools (such as virtual membership cards that connect online and offline channels).
Businesses should treat digitalization and datafication as core competencies; the value of technological tools lies in connecting the physical and virtual worlds of customer experience. Businesses should adopt and effectively utilize human-machine collaboration thinking to build an agile corporate culture, adapt to changes in the environment, and effectively demonstrate the spiritual value of their brand to consumers and society while monetizing their products, thus building a sustainable customer network.
References:
Marketing 5.0: By Philip Kotler, Chen Jiuxue, and Ivan Setiawan
Manager: An Illustrated Guide to “Scenario-Based Marketing Model”
Further Reading:
Digit Spark, part of the Zhenhao Internet Media Group, integrates its six sub-brands offering data application services to provide enterprises with comprehensive and precise optimization services across five key areas: “Industry Customer Targeting,” “Performance Optimization Strategies,” “Digital Tool Integration,” “Online Voice Cultivation,” and “Brand Value Promotion.” It drives brand success through data technology.